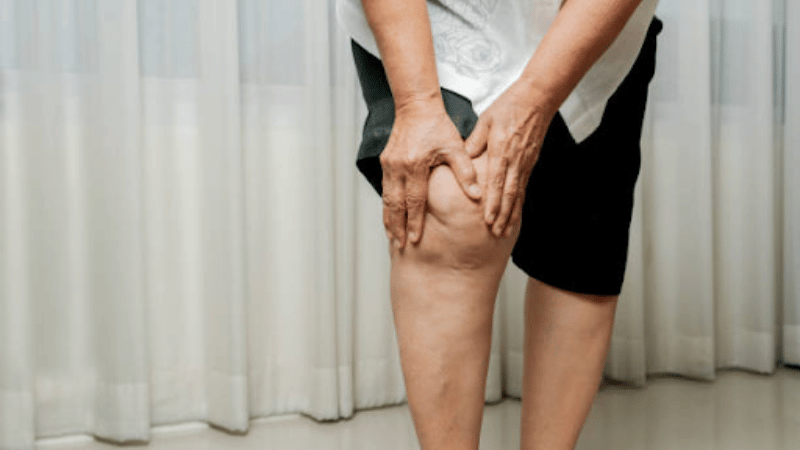
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a vascular condition caused by plaque buildup in the arteries. As the plaque accumulates, it causes the arteries to narrow, which can reduce the flow of blood, oxygen, and nutrients to the lower extremities. If left untreated, peripheral artery disease can lead to more severe complications, including but not limited to heart attack and stroke. These complications are among the leading causes of death in the United States, according to the CDC.
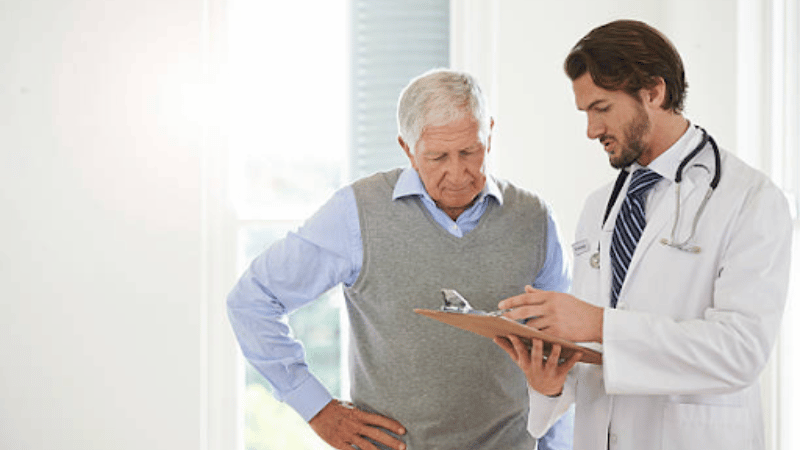
PAD patients or individuals with PAD risk factors should consider scheduling a consultation with a vascular specialist for an accurate diagnosis of peripheral artery disease. Early detection and treatment of this condition can lower your risks of developing peripheral artery disease complications.
What Are the Complications of Peripheral Arterial Disease?
According to the Oxford Academic, more than 10% of people over the age of 65 are suffering from peripheral artery disease. Some people experience severe leg pain and trouble climbing stairs, while others don’t experience any symptoms until the arteries have severely narrowed.
If PAD is left untreated, it can lead to severe complications and long-term risks for patients. A diagnosis and early treatment from a vascular specialist can help you avoid symptoms from progressing and prevent further complications.
Short-Term Complications of Peripheral Artery Disease
The short-term complications are immediate, mild complications that arise due to the narrowing of the arteries. Some common short-term complications include:
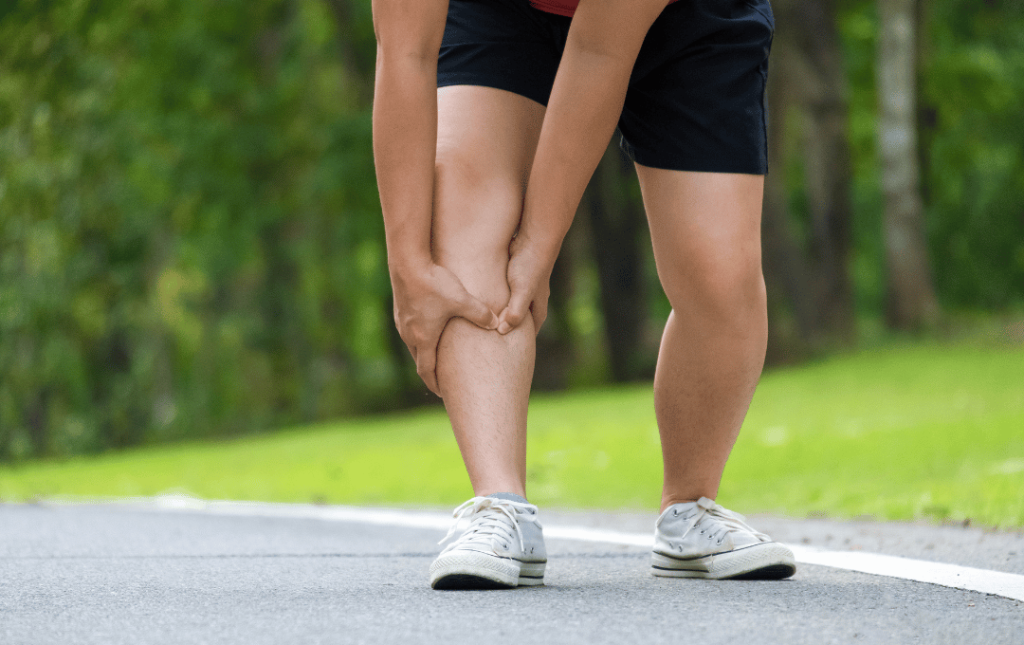
- Claudication: This type of pain and discomfort is typically caused by restricted blood flow. When left untreated, claudication can lead to blood clots or critical limb ischemia (CLI).
- Poor Wound Healing: When the arteries begin to narrow, it limits the flow of essential nutrients to the lower extremities, causing wounds to heal more slowly.
- Numbness and Tingling: Poor circulation can lead to tingling and discomfort in the legs. You may also notice your legs feel numb and heavy.
If left untreated, short-term PAD complications can impact your mobility and your day-to-day life. However, if treated early, you can lessen the severity of your symptoms and implement vascular doctor-recommended preventative steps to improve your quality of life.
Long-Term Complications of Peripheral Artery Disease
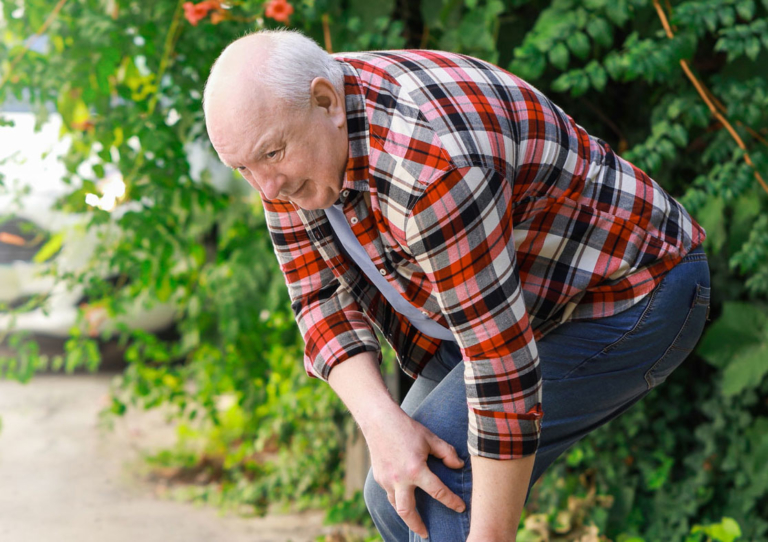
Untreated PAD can develop into more severe and fatal vascular complications, including:
- Gangrene: Gangrene is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the tissues in the extremities are deprived of nutrients. This kills the body tissue, and the affected area may need to be amputated to prevent the spread of infection to other healthy body parts. Gangrene is a common symptom of critical limb ischemia, the most advanced form of peripheral artery disease.
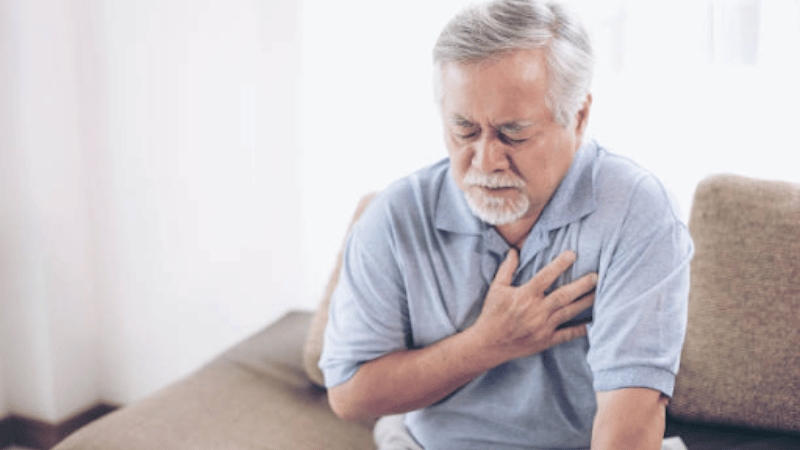
- Heart Attack and Stroke: Untreated PAD can lead to an elevated risk of cardiovascular events. The plaque buildup can impact the arteries supplying blood and nutrients to the brain and heart, causing severe conditions such as stroke or heart attack.
- Impact Other Organs: Reduced blood flow can also impact other organs in the body, including the kidneys and intestines.
Managing and Preventing PAD Complications
USA Vascular Centers provides non-surgical treatment options that can help you manage PAD symptoms and reduce the risk of long-term complications. These FDA-approved treatments include:
- Angioplasty: A small balloon is inserted into the artery and inflated, compressing the plaque against the artery wall.
- Stent Placement: After an angioplasty, a mesh stent is used to prop the artery open.
- Atherectomy: Plaque is extracted from the arterial walls using a thin tube with a specialized tip.
Since these procedures are minimally invasive, patients can benefit from a shorter recovery time and a reduction in symptoms. Receiving treatment for PAD, as well as taking medications as prescribed and making lifestyle modifications, can reduce your risk of PAD complications.
Avoid PAD Complications with USA Vascular Centers
USA Vascular Centers are here to help you get in control of your vascular health. Our vascular specialists are here to detect peripheral artery disease and recommend the best minimally invasive treatment for your condition. With our expert care and guidance, you can minimize discomfort and reduce your risk of serious PAD complications later down the line.
If you’re interested in an accurate diagnosis or looking for non-surgical PAD treatment, call us at 888.773.2193 or schedule your online appointment with our specialist.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can PAD complications be reversed?
PAD is a progressive disease that cannot be cured or reversed. However, early detection and treatment can help lessen the severity of your PAD-related symptoms and reduce your risk of long-term complications.
Does PAD Increase the risk of heart attack and stroke?
Plaque buildup can lead to poor circulation and blood flow, leading to an elevated risk of cardiovascular events.