Understanding the Differences Between PAD vs. PVD
When it comes to managing your health, it’s important to fully understand your condition. It can sometimes be confusing when doctors use terms interchangeably without disclosing what they mean.
There are subtle differences between the terms, PAD and PVD. Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) afflicts the arteries alone while peripheral vascular disease (PVD) is a broader term which includes any blood vessel including, veins and lymphatic vessels. Both are progressive disorders that narrow or block blood vessels, limiting the amount of oxygen and nutrients circulating in your body. PVD doesn’t have tissue damage on the structure of the vessel, where PAD does. This tissue damage on the walls of the arteries is caused by the accumulation of fat. These blockages can cause major health concerns if they break off and travel to another part of the body. Floating plaque can cause DVT (deep vein thrombosis) in the iliac veins, or travel up towards the brain causing a stroke. Plaque buildup in the arteries is caused by increased LDL (low-density lipoproteins, also known as “bad cholesterol”) which can cause cells to stop processing this fat, allowing it to accumulate in the bloodstream.
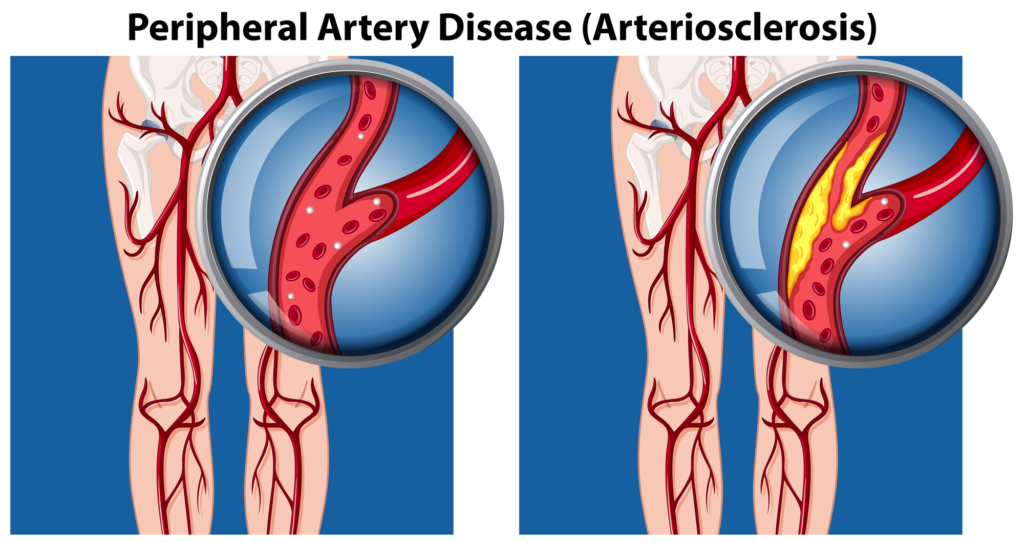
While symptoms of PAD and PVD are similar and even share some of the same symptoms there are differences.
| PAD | PVD |
| Pain or cramping in legs (muscles calf, thigh, or buttocks) during activity and disappears at rest |
Dull cramping and pain that comes and goes in the legs |
| Numbness and tingling | Heaviness or tightness in the leg muscles |
| Slow healing or non-healing sores on toes, feet, or legs |
Leg or foot that feels cool or cold to the touch compared to the other leg |
| Skin color changes | Burning sensation |
| Poor nail growth | Leg fatigue Leg or foot feeling cool or cold to the touch |
| Thinning of skin on legs | Skin color changes |
| Some people do not experience ANY symptoms | Loss of leg hair |
Medical evaluation and effective treatment are recommended to prevent further damage and more drastic events such as heart attack, stroke, or amputation. Early diagnosis of PVD and PAD will respond well to lifestyle changes such as diet, exercise, lowering cholesterol and blood pressure, controlling your blood sugar and quitting smoking. If your PAD has progressed, our vascular specialists will create a customized treatment plan that is right for you.
All of our treatments are covered by Medicare, most major health, and some Medicaid plans. To improve your quality of life, keep your independence, and your mobility call USA Vascular Centers at (855) 514-6149 to schedule your appointment today. For more information regarding our services, please visit our website www.usavascularcenters.com at any time.
References
The American Heart Association (2016, October 31). About Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD). Retrieved August 11, 2018, from https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/peripheral-artery-disease/about-peripheral-artery-disease-pad
Disease, P. V. (2016, June 30). Peripheral Vascular Disease (M. Ratini DO, MS, Ed.). Retrieved August 13, 2018, from https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/peripheral-vascular-disease#1