You’ve probably heard the terms coronary heart disease (CHD) or artery disease in connection with heart health. The two terms are sometimes used interchangeably, but the difference is that coronary heart disease is just one type of arterial disease.
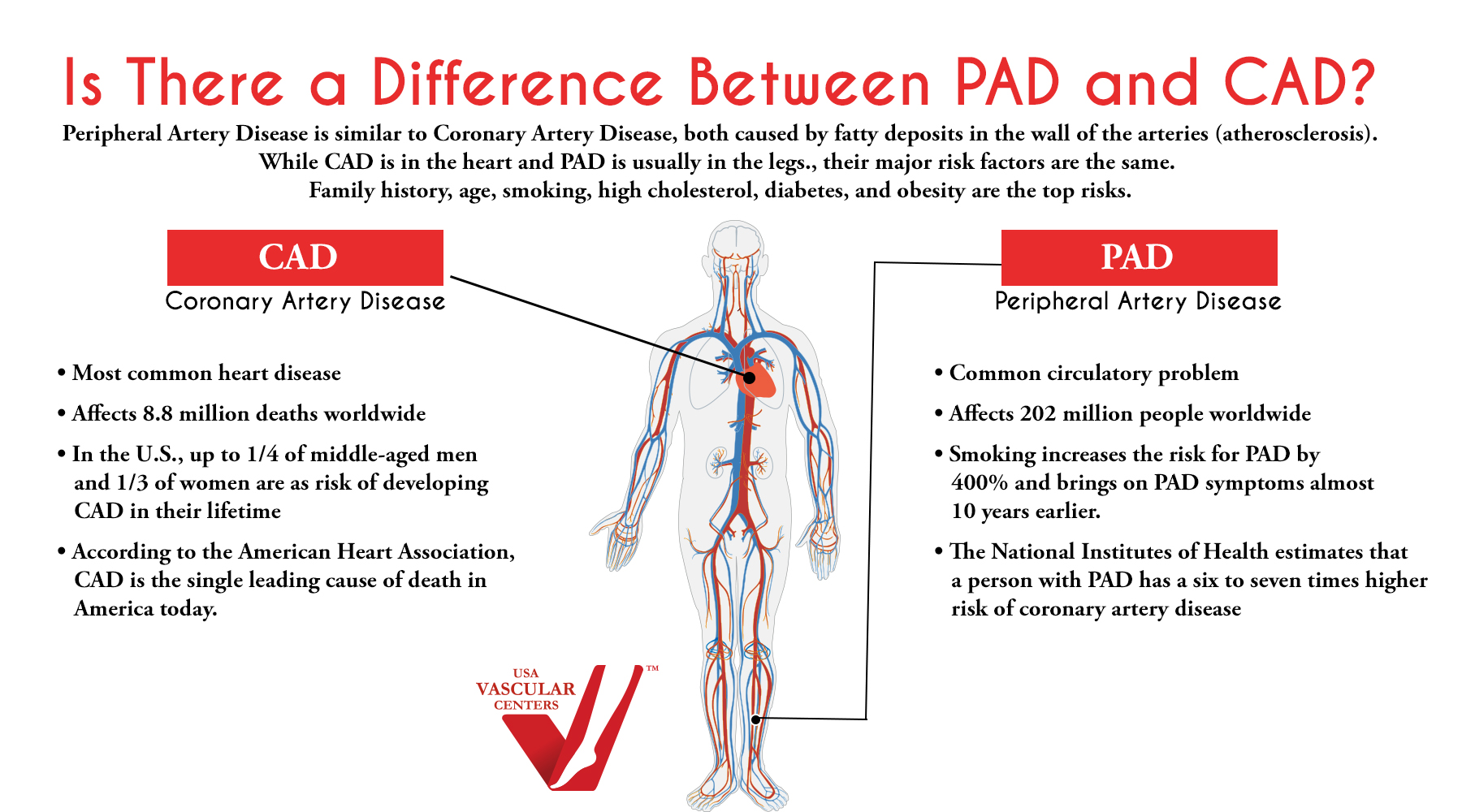
Coronary arterial disease is categorized as the narrowing or blockage of arteries, which is often linked to atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaques and cholesterol in your arteries. You may wonder, “Is coronary artery disease the same as atherosclerosis?” The answer is that atherosclerosis is what causes coronary arterial disease. It also causes other types of arterial disease, including peripheral artery disease, carotid artery disease, and renal vascular disease.
What is Coronary Heart Disease?
Coronary arterial disease (CAD) is plaque buildup in the coronary arteries. For your heart to function properly, it needs a steady supply of blood to pump through your body. Plaque buildup in coronary arterial disease makes your heart work harder to pump its blood, limiting the oxygen and nutrients passed through your heart.
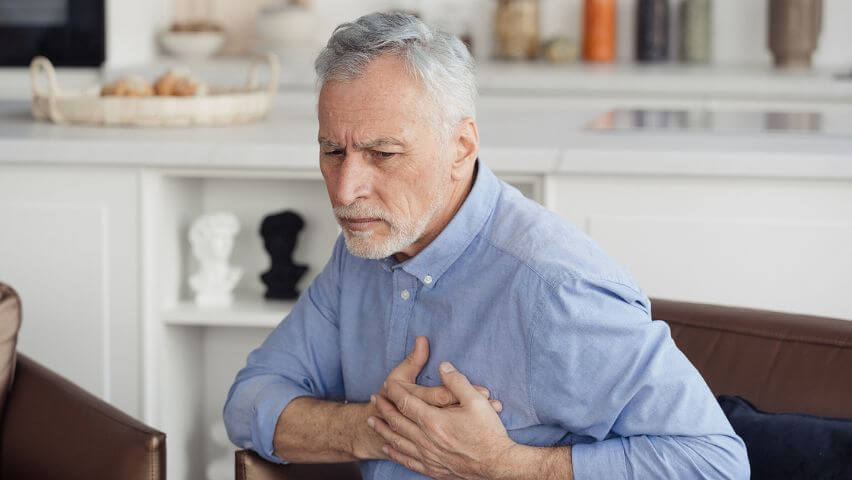
Without treatment, coronary arterial disease can cause a heart attack. This life-threatening condition happens when plaque builds up so much that it blocks the artery, stopping blood from flowing at all. Common heart attack symptoms include cold sweats, nausea, chest pain, shoulder pain, and shortness of breath. After a time, coronary arterial disease and heart attacks can lead to a weakened heart that cannot pump blood as it should (heart failure).1
If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, seek emergency medical help immediately. Schedule a consultation with one of our renowned vascular doctors at USA Vascular Centers to learn more about how atherosclerosis can impact your arteries. Our highly recommended doctors can answer questions about CAD signs and symptoms and help you understand the difference between coronary artery disease vs. peripheral artery disease.
CAD Risk Factors
Learning about the controllable risk factors of coronary arterial disease can help you take steps to prevent the onset of the disease. The most common CAD risk factors you can avoid include smoking, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, obesity, stress, and an unhealthy lifestyle.
There are risks of coronary arterial disease that are not preventable or cannot be treated. It is important to know these risk factors so you can maintain the controllable risks if you fall into any of the following categories:
- Gender: men have an increased risk over women
- Age: as your age increases, so does the risk of CAD
- Genetics: family history of heart disease
You may have already known the risk factors of heart disease, but may not be as familiar with the causes of the disease. A major cause of heart disease is atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of plaque and cholesterol in your arteries.
Many of us associate plaque with what dentists scrape off our teeth, but arterial plaque is made up of different substances like: calcium, fat, cholesterol, cellular waste, and fibrin. These substances are circulated with your blood which can eventually build up and clog your arteries.
Plaque buildup can lead to different conditions depending on where the plaque develops and which artery is affected. Common arteries that experience plaque buildup are:
- Coronary arteries: lead blood to or in the heart
- Renal arteries: supply blood to the kidneys
- Carotid arteries: provide blood to your brain, neck, and face
- Peripheral arteries: supply blood to the body (i.e., arms and legs)
Blockages in any of the above-mentioned arteries can cause issues for your body. It is more common to focus on the arteries that supply blood to your heart or brain, but blockages in the peripheral arteries can cause Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD). While there is a clear difference between coronary artery disease vs. peripheral artery disease, both are similar in that both are caused by atherosclerosis, share the same risk factors, and can lead to more serious conditions. People with PAD have a higher risk of heart attack, stroke, gangrene, or amputation.
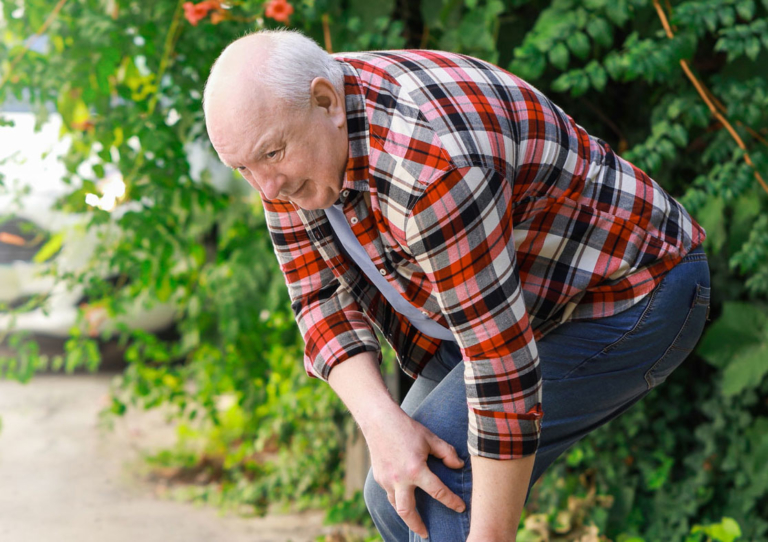
Symptoms of PAD are more common in your legs and include:
- Heaviness or cramping in your legs
- Pain in your legs that disturbs your sleep
- Sores or wounds on your legs and feet that heal slowly or not at all
- Skin color changes
- Poor hair and nail growth on legs and feet
Many people mistake PAD symptoms for normal signs of aging and put off going to the doctor. But knowing the common symptoms of PAD will alert you to the warning signs so you can seek help sooner rather than later.
Arterial disease, whether arterial heart disease or peripheral artery disease, is a dangerous condition that can affect your body differently. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, regularly going to the doctor, and paying attention to your body will help prevent arterial and heart disease. Through education and talking about our experiences, we can beat arterial diseases.
If you’re experiencing any of the symptoms of PAD, are over the age of 50, have a history of smoking or vascular disease in your family, or have diabetes, schedule an arterial check online today!
Sources Cited
[1] “Coronary Artery Disease.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, July 19, 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/coronary_ad.htm.