Your heart beats around 100,000 times a day, pumping 1.5 gallons of blood throughout your circulatory system. Blood brings essential oxygen and nutrients to your cells and carries waste out. However, if your blood vessels become damaged, your blood cannot circulate as well as it should, leading to what is commonly known as poor circulation.
What is Poor Circulation?
Your circulation system is responsible for transporting blood, oxygen, and nutrients through the body. Poor circulation is when blood flow is reduced in a specific part of the body, typically in the feet or arms.
The most common cause of poor circulation in the legs is peripheral artery disease or PAD. PAD is caused by plaque accumulation in the arteries that supply blood to your legs and feet. While this may seem like a minor issue, PAD can lead to gangrene and amputation if left untreated.
At USA Vascular Centers, our trusted vascular doctors are dedicated to raising awareness of the symptoms of poor leg circulation and providing PAD treatments to help you avoid serious complications.
Recognize the Symptoms of Poor Leg Circulation
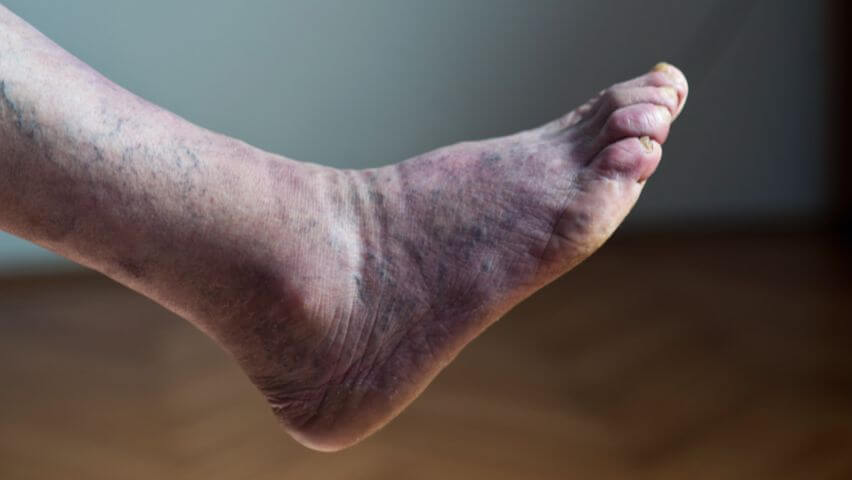
When blood flow is reduced, you’ll feel pain, numbness, and a tingling sensation in the affected part of the body. Some of the other most common symptoms of poor leg circulation in the feet and legs include:
- A feeling of pins and needles
- Coldness
- Bulging veins
- Pain when walking
- Swelling or numbness
- Weak muscles
- Swelling and edema
- Skin discoloration
- Slow-healing wounds or ulcers
Poor circulation can be harmful, especially if you ignore the warning signs. If you have any signs of poor circulation in your feet or legs, consider scheduling a consultation with a vascular specialist immediately. Depending on its severity, they’ll be able to diagnose your condition and provide the right treatment plan.
Poor circulation can be caused by various vascular conditions, including atherosclerosis, peripheral artery disease (PAD), and blood clots. The first step to treating poor circulation in the feet and legs is to meet with a doctor for a professional diagnosis.
PAD and Poor Circulation
Plaque buildup, which leads to peripheral artery disease, is the leading cause of poor leg and foot circulation. Plaque is composed of calcium, fibrin, cholesterol, fatty substances, and cellular waste. When it accumulates in the arteries, plaque can significantly restrict blood flow, causing poor circulation or even cutting off circulation completely.
Many factors contribute to plaque buildup and can put you at greater risk of developing PAD. This includes:
- Smoking: The chemicals in cigarette smoke damage your arteries, making it much easier for plaque to accumulate.
- Diabetes: Like cigarette smoke, high blood glucose levels can harm your arteries, leading to plaque accumulation and poor circulation in the legs and feet.
- High blood pressure: When you have high blood pressure, your heart pumps blood harder than it should, damaging your arteries.
- High cholesterol: Excessive cholesterol in the bloodstream gets deposited on the artery walls, creating a blockage.
Fortunately, it’s possible to manage PAD risk factors like the ones above. For example, quitting smoking can lower your risk of developing PAD and help improve the outcome of treatments for existing PAD symptoms. Diet changes, exercise, and medication can help manage diabetes, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure, lowering your risk of developing poor circulation in the legs and feet.
What Causes Poor Circulation?
While PAD is the most common cause of poor circulation in the legs and feet, there are other vascular diseases and conditions to be aware of:
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Blood clots
- Atherosclerosis
- Varicose veins
- Raynaud’s disease
- Diabetes
- Venous insufficiency
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is another serious condition that obstructs blood flow in the leg. DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the leg, impacting circulation. This clot can break away and cut off the blood flow to the lungs, causing a life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism. Signs of poor circulation in the legs due to DVT include sudden swelling, pain, or tenderness in the leg and skin that feels warmer than usual. Chest pain, difficulty breathing, pale or bluish skin, and sweating can all be signs of a pulmonary embolism. If you experience these symptoms, seek immediate medical care.
It’s important to note that poor circulation isn’t a condition by itself. Instead, it’s a symptom of a more serious condition. Conditions such as obesity, high blood pressure, and negative lifestyle choices can also contribute to poor circulation. Additionally, vascular diseases like deep vein thrombosis and atherosclerosis are critical factors that may lead to this symptom.
While changes to your lifestyle may help alleviate some of the pain associated with poor circulation in the feet and legs, it will not “cure” your condition. The best way to improve your overall health is to schedule a consultation with a vascular doctor for a diagnosis.
Prevention Tips for Poor Blood Flow to the Feet
If you’re exhibiting signs of poor blood flow to the feet, the first step would be to schedule a consultation with a vascular doctor to discuss your diagnosis and treatment plan. Outside of treatment or medication, other prevention tips that can help alleviate some of the pain associated with your symptoms of poor circulation include:
- Exercising Regularly
- Avoiding Caffeine
- Elevating your legs
- Staying hydrated
- Stretching regularly
- Prioritizing a healthy diet
- Quitting smoking
- Limiting alcohol intake
- Maintaining a healthy weight
Adjustments to your everyday life can help lessen the severity of your symptoms of poor circulation. However, these prevention tips won’t “cure” your condition. They can only help you manage or improve your condition. A vascular doctor can assess if treatment, surgery, or medication is needed.
Treatment For Poor Circulation in Legs
If you are diagnosed with PAD, your doctor may recommend an angioplasty, stent placement, or atherectomy based on the severity of your condition. These non-surgical procedures can help improve the circulation in your legs and feet and alleviate the symptoms of PAD, all with a short recovery time of one to two weeks. Some of the top treatment methods for PAD are:
- Angioplasty: This common procedure uses a catheter to guide a tiny balloon into the affected artery. The balloon is then inflated, compressing the blockage.
- Stent placement: This is a similar treatment to angioplasty, using a mesh stent to keep the artery open permanently while preventing plaque from breaking off.
- Atherectomy: This treatment uses a rotating or laser catheter to scrape away the plaque buildup within the artery.
At USA Vascular Centers, our skilled doctors perform all three of these minimally invasive treatments in our state-of-the-art outpatient centers. Our centers are certified by the Accreditation Association for Ambulatory Health Care, demonstrating our commitment to the highest standards in patient care.
Suppose you don’t know whether PAD or another condition is causing poor circulation in your legs or feet. In that case, our doctors can perform the following diagnostic tests to determine the cause: ankle-brachial index (ABI) tests and angiograms:
- Ankle-brachial index test: Your vascular specialist measures the blood pressure in your arm and compares it with the blood pressure in your ankle. This helps determine whether PAD is the cause of poor circulation in the legs.
- Angiogram: Contrast dye is injected into the vascular system, which our vascular specialists use (in conjunction with X-ray imaging) to find the exact location of a blockage.
If you’re unsure what’s behind the poor circulation in your legs and feet, contact our team at 888-773-2193 or schedule an appointment online. Our vascular doctors are here to listen to your concerns and help you find answers about poor leg circulation.
Frequently Asked Questions About Poor Circulation
Is poor circulation in the legs serious?
Poor blood circulation in the legs can have potentially serious complications. Low blood supply to the legs can eventually damage the nerves and tissues in the leg. Nerve damage can lead to altered sensation in the legs, including numbness and tingling.
Can you reverse poor circulation in the legs and feet?
In many cases, the goal of treatment is not reversal but management of the condition. For this reason, it’s more beneficial to focus on prevention than reversal. You can help lower your risk of developing poor leg circulation by staying active, eating a nutritious diet, and avoiding smoking. If you have diabetes, managing your condition well can go a long way toward helping prevent impaired circulation.
How do you fix poor circulation in the legs?
The first step in addressing poor circulation in your feet and legs is visiting a vascular specialist to diagnose the cause accurately. From there, you can work with your provider to create and maintain a treatment plan based on your health history and the cause of the poor circulation in your legs.
What does poor circulation in your feet and legs look like?
Pain or cramping in the legs while walking that goes away when you rest can be an early sign of PAD. Other signs to watch for include cold, clammy feet and a pale or bluish discoloration of the feet and toes.
Poor circulation also produces dry, cracked skin on the legs, inhibits hair and nail growth, and prevents open wounds from healing. If you notice these symptoms, schedule a consultation with a vascular specialist.