Have you been diagnosed with peripheral artery disease (PAD)? If so, a minimally invasive treatment called an angioplasty to improve blood flow through the leg arteries may be recommended. One common component of angioplasty is using a stent, a small, mesh-like tube that helps prop open the affected artery. But with so many different types of stents available, it can be overwhelming to understand your options.
Are you considering angioplasty for PAD? In this article we’ll explore the five most common types of leg stents used in angioplasty procedures. We’ll also discuss the benefits of a stent placement and help you make informed decisions about your treatment.
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) can be treated using various options, depending on its severity and location. Treatment options typically focus on improving blood flow to affected areas, managing symptoms, and preventing further complications.
These can include lifestyle changes, medications to control symptoms and prevent blood clots, and more advanced procedures like angioplasty, stent placement, or surgical interventions. Each treatment aims to restore circulation and reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, or other serious health issues.
What is a Peripheral Artery Angioplasty?
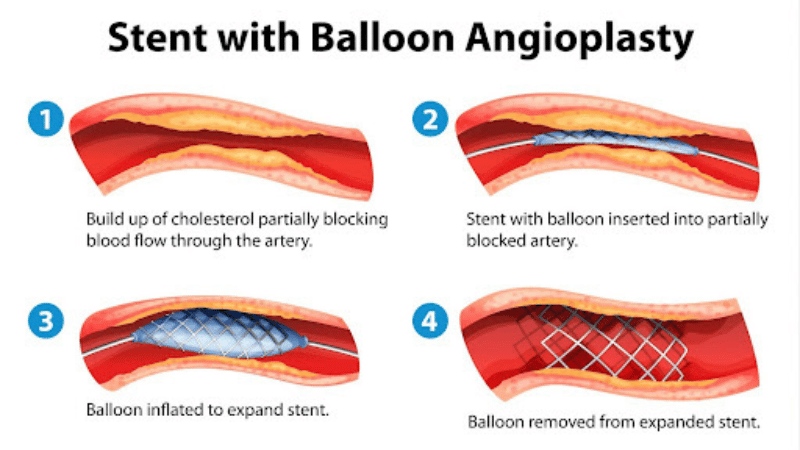
A peripheral artery angioplasty is a minimally invasive, non-surgical treatment that helps widen blocked arteries to improve blood flow. During an angioplasty procedure, a vascular doctor inserts a balloon, stent, or laser into the artery to clear a path through the plaque. For a stent angioplasty, a stent is placed inside the affected artery to keep it propped open after the plaque has been compressed or removed. The recovery time after arterial stent placement is minimal. Most patients can return home the same day and return to normal activities after about a week.
Why are Stents Used During an Angioplasty?
There are many advantages to an angioplasty stent procedure. Some benefits PAD patients may experience include:
- Restore Blood Flow: A stent placement after an angioplasty holds the artery open, helping restore blood flow, oxygen, and nutrients to the legs and feet.
- Improve Mobility: Stents can help reduce claudication and improve mobility. Many patients notice a difference in less than a week after the procedure.
- Reduce the Risk of Serious Complications: Since the placement of stents in the legs can treat poor circulation, this can help you avoid ulcers and infections caused by PAD. It can also help lessen the severity of PAD symptoms and improve your quality of life.
- Prevent the Progression of PAD: While PAD cannot be reversed, minimally invasive treatments can help prevent the progression of the disease.
5 Types of Stents Used to Improve Blood Flow
If you have PAD, the first step is to schedule a consultation with a vascular specialist. They’ll assess your condition and determine if an angioplasty stent procedure is right for you. If so, they may use one of the following five types of vascular stents.
1. Balloon Expandable Stents
During a balloon stent angioplasty procedure, an interventional radiologist will place the balloon inside the artery. The balloon expands and pushes the plaque against the arterial walls. A stent is then placed to keep the artery propped open. This is one of the most commonly used vascular stents for peripheral artery disease.
2. Self-Expanding Stents
These vascular stents are made of a mesh-like material designed to expand on its own once it’s placed in the artery. Self-expanding stents are commonly used in the lower limbs. They are durable and flexible, which is ideal for everyday movement.
3. Bare metal stents (BMS)
Bare metal stents are simple, effective stents made of stainless steel or cobalt-chromium. This type of stent tends to be a more affordable option and is ideal for elderly patients. BMSs are used on PAD patients but can also be used to treat coronary artery disease or urologic disease conditions.
4. Bio-Engineered Stent (BES)
These vascular stents are coated with antibodies that promote natural healing in the artery. BESs are typically used for coronary artery disease (CAD) rather than PAD. This is because stents in the legs need to be more flexible to deal with movement.
5. Drug-Eluting Stent (DES)
DESs are made of stainless steel or cobalt-chromium and coated with a medication to prevent future artery blockages. This type of vascular stent is commonly used to treat the superficial femoral artery or popliteal artery in PAD patients.
Schedule a Consultation With USA Vascular Centers
Don’t let PAD slow you down. Our interventional radiologists are experts in diagnosing and treating your PAD symptoms. We’ll work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Is an angioplasty stent procedure the right choice for you?
Schedule an online consultation today or call us at 855.615.2555 to find out. We will evaluate your condition and discuss your options.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Peripheral Artery Disease?
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a progressive vascular condition caused by excess plaque in the arteries. When the plaque starts to build up, the arteries begin to narrow, restricting the flow of blood, oxygen, and nutrients to the lower extremities. PAD can impact mobility and cause chronic leg pain or numbness. While PAD is not reversible, minimally invasive treatments are available to help reduce the severity of the symptoms.
What are the most common types of stents used in peripheral artery angioplasty?
Balloon-expandable and bare metal stents (BMS) are the two most commonly used vascular stents for PAD. During a consultation for PAD treatment, a vascular doctor will assess the patient’s symptoms, age, and risk factors to determine which option is best.
How long do stents last after peripheral artery angioplasty?
Stents can be a long-term solution for PAD, often lasting around 5-10 years. However, their lifespan can vary depending on factors like your overall health and lifestyle. Diet, smoking, drinking, and exercise can significantly improve outcomes. Schedule a consultation with a vascular doctor today to discuss your personalized lifestyle recommendations and learn more about how to care for your stent.
Are there any alternatives to stenting for treating PAD?
While stents are often used in PAD treatment, other options are available depending on the severity of the condition. In some cases, balloon angioplasty can be performed without a stent. Atherectomy is a technique that involves removing plaque from the artery with a special device. Both options are minimally invasive procedures that can help improve blood flow to your legs without the need for surgery.